The term “carbon footprint” is an intriguing concept associated with greenhouse gases. A carbon footprint is a measure of the amount of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, that are emitted by the activities of a person, organization, product, or country. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and climate change. Therefore, reducing the carbon footprint is important for mitigating the negative impacts of climate change on humans and the environment.
These direct and indirect emissions are categorized into three broad scopes:
Scope 1: All direct Greenhouse gas emissions.
Scope 2: Indirect Green House Gas emissions from purchased electricity, heat or steam consumption.
Scope 3: Other indirect emissions, such as the extraction and production of purchased materials and fuels, transport-related activities in vehicles not owned or controlled by the reporting entity, electricity-related activities (e.g. T&D losses) not covered in Scope 2, outsourced activities, waste disposal, etc
The increase in worldwide emissions from the middle of the 18th century to the present is seen in this graph. It is evident that emissions were extremely low before the Industrial Revolution. Emissions growth remained very moderate until the middle of the 20th century. The globe released six billion tons of CO2 in 1950. This nearly doubled to more than 22 billion tons by 1990. Our annual emissions have risen steadily over the past few years, reaching over 34 billion tons. Although the rate of increase in emissions has decreased recently, it has not yet reached its maximum
Excluded are: short-cycle biomass burning (such as agricultural waste burning), large-scale biomass burning (such as forest fires), and carbon emissions/removals of land-use, land-use change and forestry. CO2 Emissions by Sector CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuel for the following uses:
Global Fossil CO2 Emissions by Sector :
Power Industry: 38.5 %
Non-combustion: 10.0 %
Other industrial combustion: 21.2 %
Transport: 20.9 %
Buildings: 9.4 %
Our Study:
- The study is based on primary sources from Google survey form and offline survey secondary sources collected from the Census of Inda, the United Nations (UN) population estimate, NITI Aayog, Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), the World Bank, and Reserve Bank of India (RBI), etc. The available data in various parameters like human population, urbanization, carbon storage/emission, and socio-economic indicators like gross state domestic product (GSDP), poverty index, human development, etc. have been compiled state-wise and presented for statistical inferences. In our survey, there are 52.2% of men and 46.4% are female.
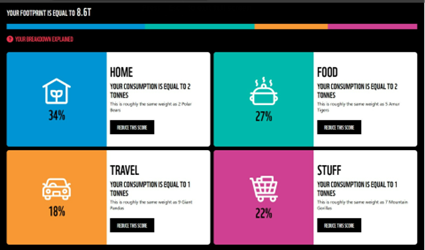
- In the survey, the average age of individuals is 22 years. our carbon footprint is equal to 8.6 tonnes for better understanding we consider the UK(United Kingdom) for comparison. and the average phone usage is 5 hours a day. Carbon footprint for 5 hours a day≈43kg CO2e per year, Please note that this is a rough estimate, and actual carbon footprints can vary based on factors specific to your phone and usage.
- In January 2022, global per capita carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions vary significantly from country to country. The worldwide average per capita CO2 emissions were around 4.8 metric tons per person per year. However, these numbers can change over time as countries adopt different energy sources and implement climate policies. If India’s per capita CO2 emissions are 8.6 tonnes per year, this would be higher than the global average. It suggests that, on average, each person in India is responsible for emitting more CO2 than the global per capita average.
- It’s important to consider that these figures are subject to change, and updated data should be consulted for the most accurate comparisons. Additionally, different sources may provide slightly different figures based on their methodologies and data sources.
- Efforts to reduce per capita emissions often involve transitioning to cleaner energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing policies that promote sustainable practices. It’s worth noting that per capita emissions are often used as a metric to assess a country’s contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions and its progress toward mitigating climate change.

HOW TO REDUCE YOUR CARBON FOOTPRINT?
Carbon footprint can be reduced and handprint can be increased by changing our lifestyle and following some simple tips mentioned below:
- Reducing waste
- Saving electricity
- Recycling /saving water
- Saving fuel and reducing emissions
- saving paper
About the Author:
Aayan Abdul Mannan Shaikh.
FYBSC IT- Student of Thakur College of Science and Commerce, Mumbai
Phone:- 9421297970
Email:- Aayan.tcsc@gmail.com